ERP Knowledge Base
How to manage frequent engineering changes (ECO/ECR/ECN) effectively?
Features of Concurrent Design and Manufacturing
1
Rapid specification changes
2
Multiple specification changes
3
Long production cycles
4
Difficult inventory management
5
Managing numerous product codes
6
High customization rates
7
Low volume, high variety production
8
High technical barriers
9
Challenges in quality control
Problems of Concurrent Design and Manufacturing
1
How to handle excess inventory?
2
How does the production scheduling work for changes?
3
How to process a massive volume of change orders manually?
4
How to coordinate with suppliers for changes when orders are already placed?
5
How to make changes to already purchased materials?
6
How to handle changes when goods have already been received?
7
How to handle changes to materials that have already been issued?
8
How to handle changes to products that have already been produced?
How to manage concurrent design and manufacturing?
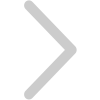
Intelligent Change Management Platform
- Providing ECN(Engineering Change Notice) change operations for adding/removing/replacing/modifying components.
- Change approval process
- Updating the BOM (Bill of Materials) structure table in real time.
- Initiating order changes from the sales representative
Triggering an end-to-end change process.
- Automatically synchronize the generation of work orders and purchase order changes.
- Conduct audits to check completed documents.
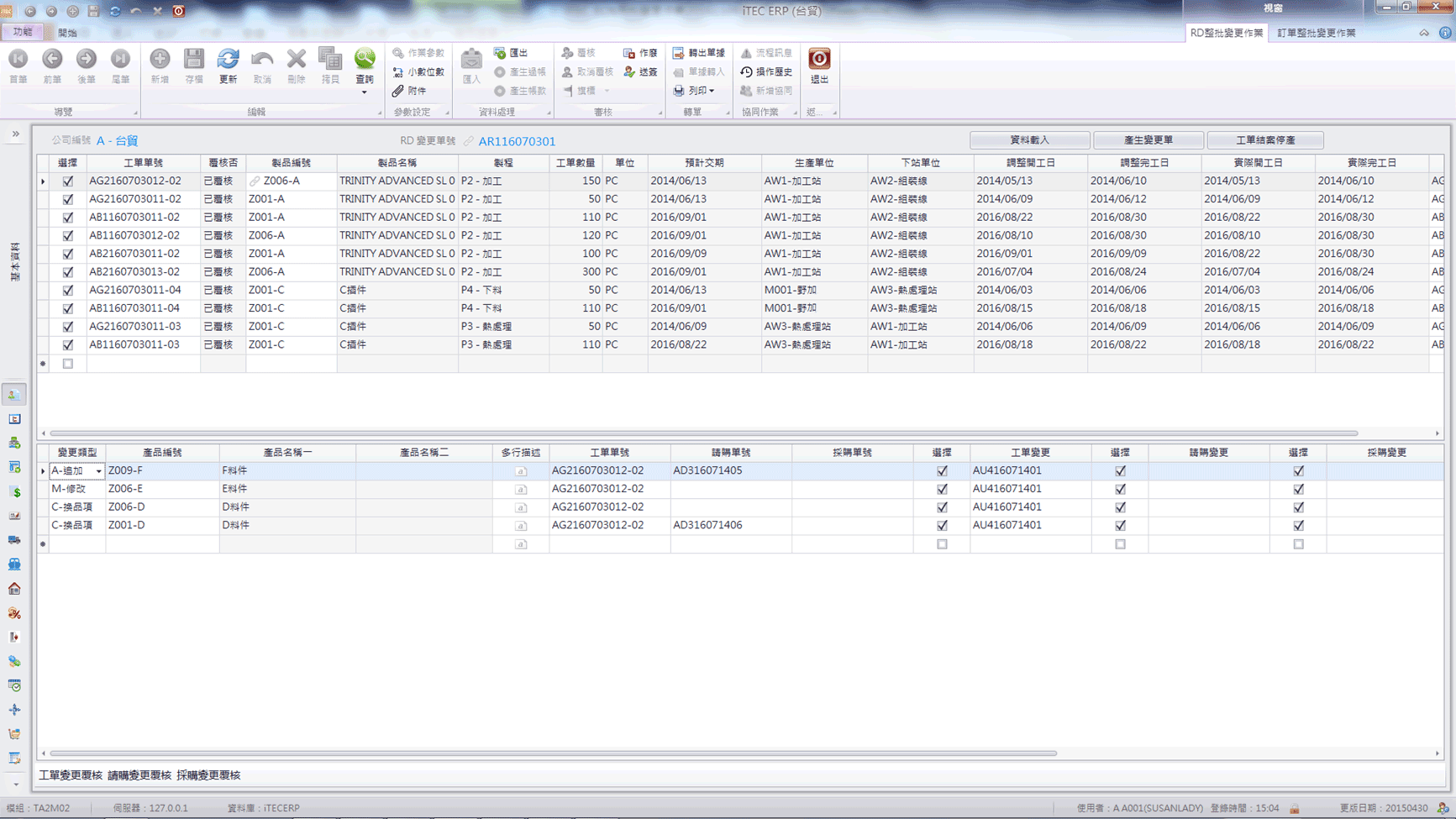
Change Dynamic Analysis Platform
- Provide the number of material changes within a specific range.
- Provide the number of product changes within certain intervals.
- Provide the number of changes for a particular order.
- Analyze change responsibility attribution.
Operational Issues in Practice and Improvement Directions
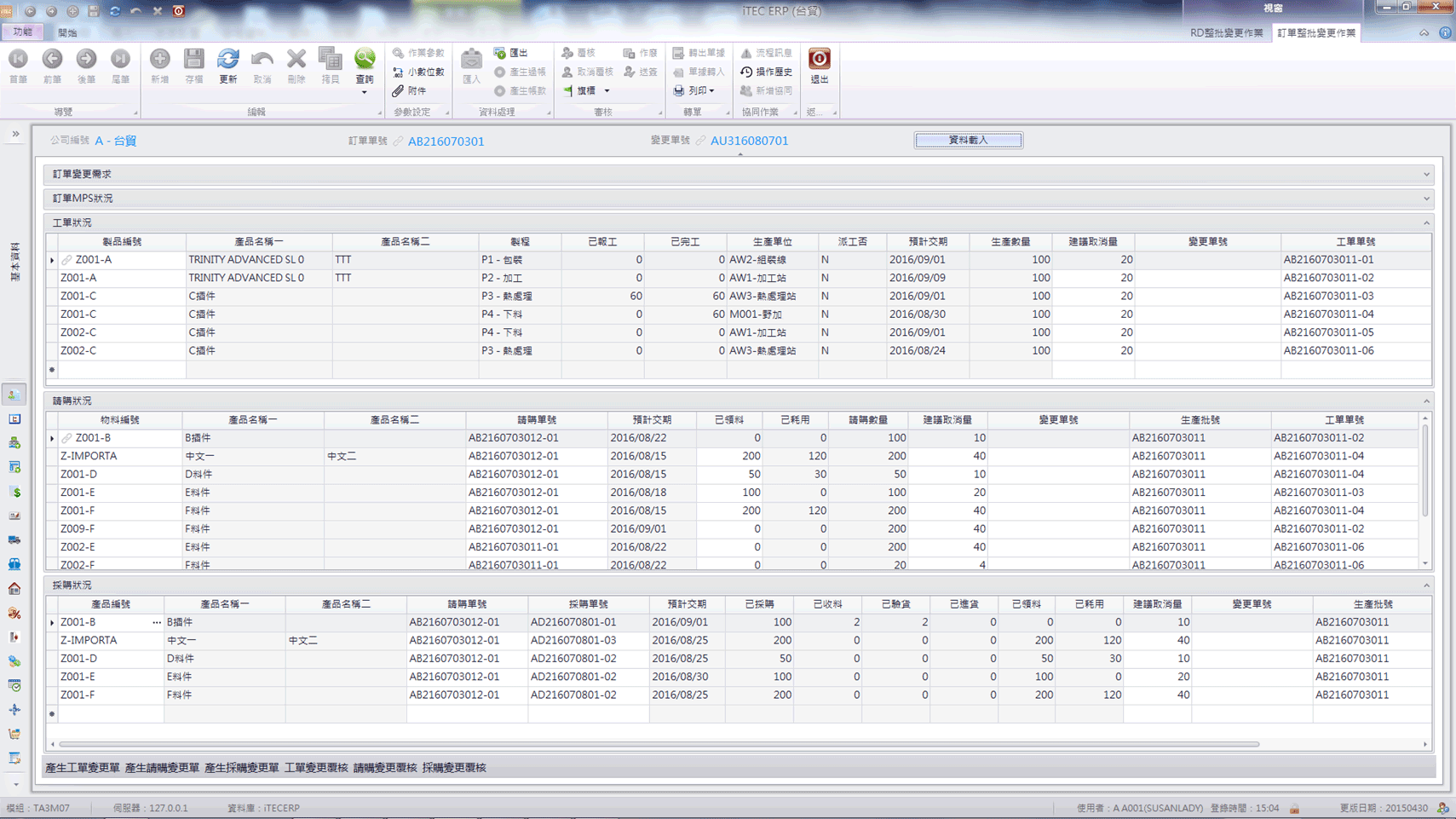
1
When R&D initiates material change operations through batch processing, the system automatically generates related change orders.
2
After change orders are reviewed, the system automatically updates and adjusts the documents, creating a comprehensive historical trail.
3
Regularly auditing inventory or utilizing intelligent inventory analysis to determine when quantities with an age exceeding a certain number of days can be replaced.
4
Analyzing the cost of failures caused by statistical change data.
5
Using statistical data on changes from various perspectives such as customer, order type, product type, etc., as a basis for improvement.
Related Information

How to rapidly consolidate the financial accounts of multiple companies within a group?

ERP operational model in different industry?

How to manage complex and frequently changing materials?
Breaking News

 Previous Article
Previous Article